- Home
- About Us
- Our Curriculum
- Subjects
- Maths
Maths
BackHead of Subject
Mr S Bodman
Teaching Staff
Ms C Morgan (Vice Principal)
Ms H Riding (Assistant Principal)
Mr I Rossiter (Assistant Principal)
Dr D Davies
Ms I Wright
Mr T Columbine-Hyde
Mr J O’Halloran
Curriculum Rationale
Our maths curriculum involves all students learning a body of knowledge relating to the skills and applications of maths.
Maths is essential to everyday life, critical to science, technology, and engineering, and necessary for financial literacy and most forms of employment. A high-quality mathematics education, therefore, provides a foundation for understanding the world, the ability to reason mathematically, an appreciation of the beauty and power of mathematics, and a sense of enjoyment and curiosity about the subject.
As our students secure knowledge and gain skills and the ability to apply them, they will learn how maths can be used to solve problems, analyse data models and predict outcomes.
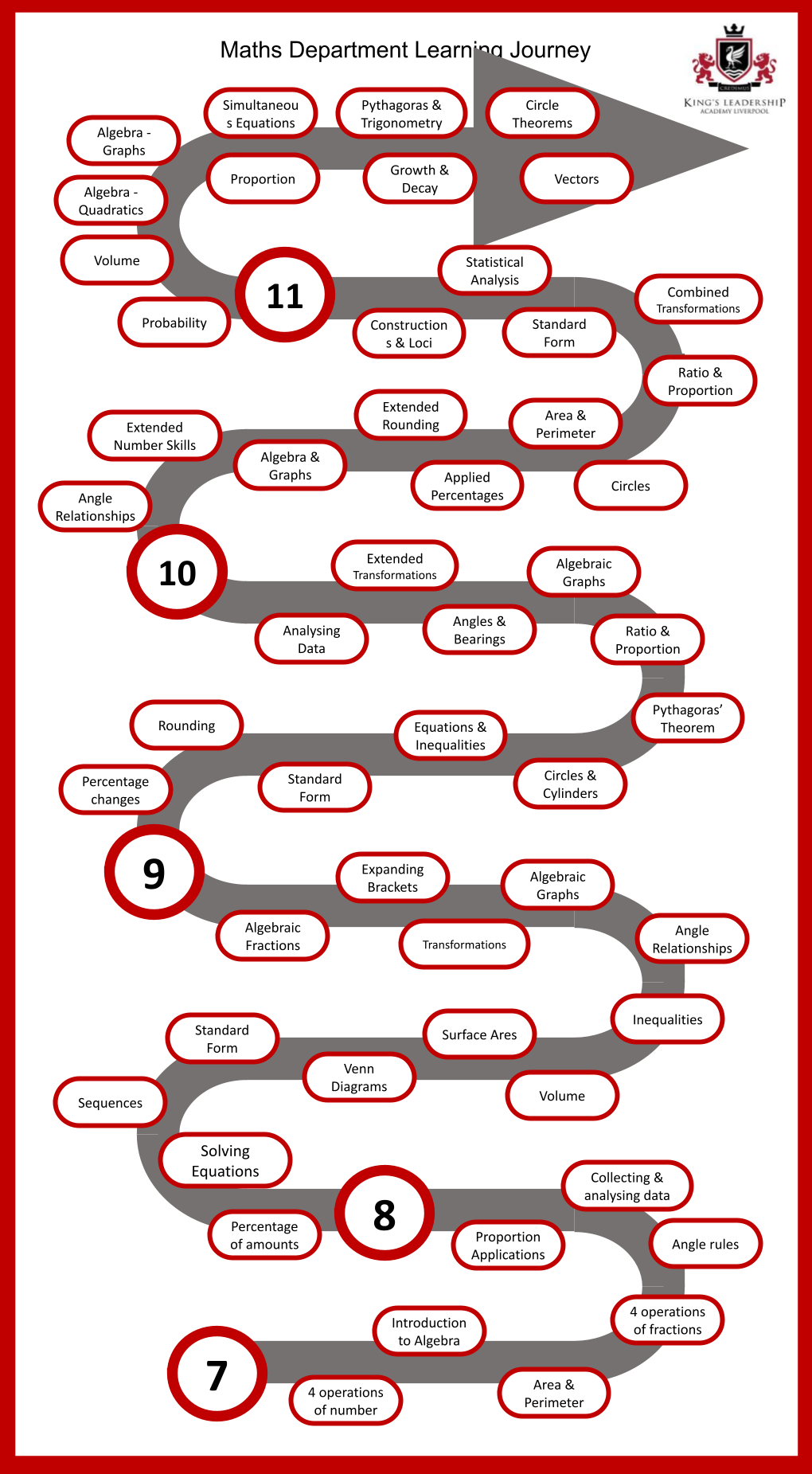
KS3 (Years 7-9)
Year 7
Topics
- Foundational topics in mathematics, starting with number sense, including addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division
- Calculations with negative numbers, order of operations, and move on to algebraic concepts such as expressions, substitution, and solving equations.
- Other key areas include understanding time, measures, and basic geometry, such as properties of shapes, perimeter, area, and angles.
- Focus on fractions, learning how to write, compare, and calculate with them.
- Data representation, probability, and understanding averages.
Skills
- Calculate fluently with all four operations.
- Work with fractions and percentages.
- Develop algebraic reasoning skills, including simplifying expressions and solving basic equations.
- Enhance geometry skills, such as measuring and calculating area and perimeter.
- Introduce data handling: interpret charts, calculate averages, and understand probability.
- Build foundational skills for more complex mathematical problem-solving in future years.
Year 8
Topics
- Extend understanding of percentages, including percentage change.
- Develop skills in ratios and algebra, including solving equations and using index laws.
- Explore geometry topics such as scale diagrams, area, volume, 3D shapes, and nets.
- Learn new concepts like significant figures, standard form, and inequalities.
- Review foundational topics, including factors, multiples, and prime numbers.
- Advance algebraic manipulation with expanding brackets and algebraic fractions.
Skills
- Develop critical skills for transitioning into abstract mathematical thinking.
- Sharpen problem-solving abilities with ratio and percentage calculations.
- Increase algebraic fluency through more complex equations and expressions.
- Enhance geometrical reasoning with surface area, volume, and transformations.
- Improve data handling and interpretation skills.
- Work with Venn diagrams and represent data graphically.
Year 9
Topics
- Consolidate and expand knowledge of fractions, decimals, and percentages.
- Study advanced topics like probability, standard form, and rounding.
- Deepen algebraic concepts with rearranging formulas, solving quadratic equations, and plotting quadratic graphs.
- Advance geometry skills with constructions, circles, cylinders, and Pythagoras’ theorem.
- Explore ratios and proportions in greater depth.
- Develop graphing skills with motion-time and compound measures.
Skills
- Build on foundational skills from earlier years.
- Develop a more analytical approach to mathematics.
- Refine algebraic manipulation skills, including rearranging formulas and solving quadratic equations.
- Enhance geometrical understanding with Pythagoras’ theorem and circle theorems.
- Advance understanding of ratios, proportions, and data handling.
- Prepare for the increased rigour of GCSE mathematics.
Assessment
Half Termly Knowledge and Skills Assessment based on topics that have been taught
GCSE (Years 10-11)
Year 10
Topics
- In Year 10, students build on foundational topics such as angles, bearings, and number operations, with the Higher curriculum introducing more complex concepts like surds.
- Algebra progresses from basic operations to more advanced topics, including linear graphs and detailed work with fractions and decimals.
- Geometry focuses on perimeter, area, properties of polygons, transformations, congruence, similarity, and constructions, with the Higher course adding greater depth.
- Ratio and proportion are explored comprehensively, alongside statistical measures and real-life graphs, ensuring students develop a thorough and well-rounded understanding.
Skills
- Develop problem-solving skills in numbers, geometry, and algebra, with a focus on sequences, equations, and standard form.
- Solidify geometrical reasoning through angles, polygons, transformations, and real-life graphs.
- Enhance proportional reasoning and statistical measures essential for GCSE exams.
- Refine algebraic manipulation skills and deepen understanding of geometry and number theory, including surds.
- Gain proficiency in interpreting and constructing various types of graphs and applying mathematical concepts to real-world situations.
- Advance statistical and geometric skills to prepare for demanding GCSE Higher Tier exams.
Year 11
Topics
- Review key topics such as probability, volume, and quadratic equations, with the Higher course including advanced algebra involving rearranging formulae and identities.
- Focus on graphical representation, including scatter graphs, sketching graphs, and transforming functions.
- Study inequalities, vectors, and advanced geometry topics like Pythagoras’ theorem, trigonometry, and circle theorems.
- Explore growth and decay, with the Higher curriculum adding numerical methods, gradients, rates of change, and areas under curves.
- Prepare for GCSE exams by mastering foundational and advanced mathematical concepts.
Skills
- Develop crucial skills such as solving quadratic equations, interpreting inequalities, and sketching graphs.
- Deepen understanding of geometry through Pythagoras’ theorem, trigonometry, circle theorems, and transformations.
- Reinforce algebraic skills with simultaneous equations, graph sketching, and advanced manipulations, including calculus for Higher-level students.
- Focus on real-life applications, such as growth and decay models, numerical methods, and mathematical problem-solving.
- Build fluency and problem-solving ability essential for final GCSE exams and progression to A-Level mathematics.
Assessment
AQA GCSE Mathematics Specification
The AQA GCSE Mathematics (8300) specification assesses students through three examination papers, each contributing equally to the final grade. The content areas and their approximate weightings differ between the Foundation and Higher tiers as follows.
|
Foundation |
Higher |
|||
|
Number |
25 % |
15 % |
||
|
Algebra |
20 % |
30 % |
||
|
Ratio, Proportion, and Rate of Change |
25 % |
20 % |
||
|
Geometry and Measures |
15 % |
20 % |
||
|
Probability and Statistics |
15 % |
15 % |
||
Each tier comprises three papers:
- Paper 1: Non-calculator
- Paper 2: Calculator
- Paper 3: Calculator
All papers are 1 hour and 30 minutes long, contain 80 marks, and collectively account for 100% of the GCSE Mathematics assessment. The distribution of content across these papers reflects the weightings specified above.
Clubs & Trips
Year 11 GCSE Revision
- Every lunchtime
- Dr D Davies
Careers
Successful maths students have a wide range of career opportunities due to the analytical, problem-solving, and quantitative skills they develop. Here are some possible career paths:
1. Engineering: Fields such as civil, mechanical, electrical, and software engineering heavily rely on mathematical principles, especially calculus, algebra, and geometry.
2. Finance and Banking: Careers in financial analysis, investment banking, and accountancy often require strong mathematical skills for data analysis, risk assessment, and financial modeling.
3. Data Science and Analytics: Data scientists use statistical and mathematical models to interpret large datasets, helping companies make informed decisions. This field is growing rapidly in sectors like technology, healthcare, and marketing.
4. Actuarial Science: Actuaries use mathematics, particularly statistics and probability, to assess financial risks in insurance, pensions, and investments.
5. Computer Science and Programming: Mathematics forms the foundation of algorithms, coding, and software development. Many computer scientists and programmers have strong backgrounds in maths.
6. Research and Academia: A career in teaching or academic research can involve working on theoretical or applied mathematical problems, contributing to developments in science, technology, and economics.
7. Architecture: Architects use geometry, calculus, and trigonometry in the design of buildings and structures, ensuring functionality and aesthetics while following precise measurements.
8. Economics and Econometrics: Economists use mathematical models to understand and predict economic trends, market behaviour, and the impact of policy decisions.
9. Statistics: Statisticians work in a range of fields, from government and healthcare to business, analysing data to help make strategic decisions.
10. Cryptography and Cybersecurity: Cryptographers use advanced mathematics to encrypt data and protect sensitive information, a key role in national security and the tech industry.
Homework & Revision
Homework
|
KS3 |
Set day: |
Friday 2pm |
||
|
Due day: |
Thursday 9am |
|||
|
Format/platform: |
SPARX Maths |
|||
|
Y10 |
Set day: |
Friday 2pm |
||
|
Due day: |
Thursday 9am |
|||
|
Format/platform: |
SPARX Maths |
|||
|
Set day: |
Wednesday |
|||
|
Due day: |
Monday |
|||
|
Format/platform: |
Weekly Worded Questions – Paper copy |
|||
|
Y11 |
Set day: |
Friday 2pm |
||
|
Due day: |
Thursday 9am |
|||
|
Format/platform: |
SPARX Maths |
|||
|
Set day: |
Wednesday |
|||
|
Due day: |
Monday |
|||
|
Format/platform: |
Weekly Worded Questions – Paper copy |
|||
|
Set day: |
Wednesday |
|||
|
Due day: |
Monday |
|||
|
Format/platform: |
Part of GCSE Paper – Paper copy |
|||
Revision
Here are some excellent websites to help pupils revise for their Maths GCSE:
1. BBC Bitesize
This is a comprehensive resource offering revision guides, videos, and quizzes for both Foundation and Higher GCSE Maths. It's easy to navigate and covers all the key topics.
2. Corbettmaths
Known for its 5-a-day practice questions, worksheets, and videos, Corbettmaths is an excellent resource for GCSE revision. It offers both Foundation and Higher Tier materials and includes exam-style questions.
3. Maths Genie
This site provides free GCSE resources, including past papers, mark schemes, revision guides, and topic-specific exam questions. It’s great for targeted revision by topic.
These websites offer a combination of videos, worksheets, and interactive quizzes, making revision engaging and effective for pupils preparing for their Maths GCSEs
Wider Reading
Wider reading can greatly enhance a student's understanding and appreciation of Maths, helping them connect concepts to real-world applications and develop critical thinking skills. Here are some recommended books and resources that support GCSE-level maths:
1. "The Simpsons and Their Mathematical Secrets" by Simon Singh
This book explores how maths is embedded in popular culture, particularly in the famous TV show *The Simpsons*. It’s an engaging way for students to see mathematical concepts in everyday life.
2. "How to Solve It" by George Pólya
A classic book on problem-solving techniques in mathematics. It teaches students how to approach mathematical problems systematically, which is a valuable skill for tackling challenging GCSE questions.
3. "Alex’s Adventures in Numberland" by Alex Bellos
A fun and accessible exploration of numbers and mathematics, this book covers a wide range of topics from simple arithmetic to complex theories, making it ideal for broadening a student’s mathematical horizons.
4. "The Number Devil: A Mathematical Adventure" by Hans Magnus Enzensberger
This is a great book for younger readers or those who want to build confidence in maths. It presents complex mathematical ideas in a fun and understandable way, using stories and characters.
5. "Fermat’s Last Theorem" by Simon Singh
This is a deeper dive into one of the most famous theorems in maths. Although more advanced, it’s an inspiring read that shows the persistence and beauty involved in mathematical discovery.
6. "The Music of the Primes" by Marcus du Sautoy
This book delves into the mysterious world of prime numbers, providing a fascinating look at how they’ve puzzled and inspired mathematicians for centuries. It’s great for students interested in the abstract side of maths.
7. "Mathematics: A Very Short Introduction" by Timothy Gowers
Part of the *Very Short Introductions* series, this book offers a concise yet insightful look into the world of mathematics, including its history, philosophy, and key concepts.
8. "Why Do Buses Come in Threes?" by Rob Eastaway and Jeremy Wyndham
This book takes everyday phenomena and explains them using mathematics, making it a great resource for students who want to see how maths applies to real life.
9. "Maths on the Back of an Envelope" by Rob Eastaway
A practical book that shows how estimation and quick maths can be useful in real-life situations. This can help GCSE students develop mental maths and problem-solving skills.
10. Magazines & Journals:
- "Plus Magazine": A great resource for articles on current developments in maths, real-world applications, and interviews with mathematicians.
- "New Scientist": This magazine often covers the mathematical sciences, linking them to developments in physics, engineering, and computer science.
11. Websites for Broader Mathematical Learning:
- NRICH : Offers problem-solving activities and puzzles that stretch mathematical thinking beyond the GCSE syllabus.
Learning Journey