- Home
- About Us
- Our Curriculum
- Subjects
- Design and Technology
Design and Technology
BackHead of Subject
Mr M Stavrinou
Teaching Staff
Ms R Evans
Ms S Burton Nickson
Curriculum Rationale
Design and technology is a multidisciplinary field that combines creative design processes with practical engineering and technological skills. It focuses on solving real-world problems by developing innovative products, systems, or services.
This subject covers areas such as product design, materials, manufacturing processes, electronics, and digital technologies. Through iterative design, prototyping, and testing, it encourages problem-solving, critical thinking, and creativity, fostering skills in engineering, construction, and technological application for industries like manufacturing and infrastructure development.
KS3 (Years 7-9)
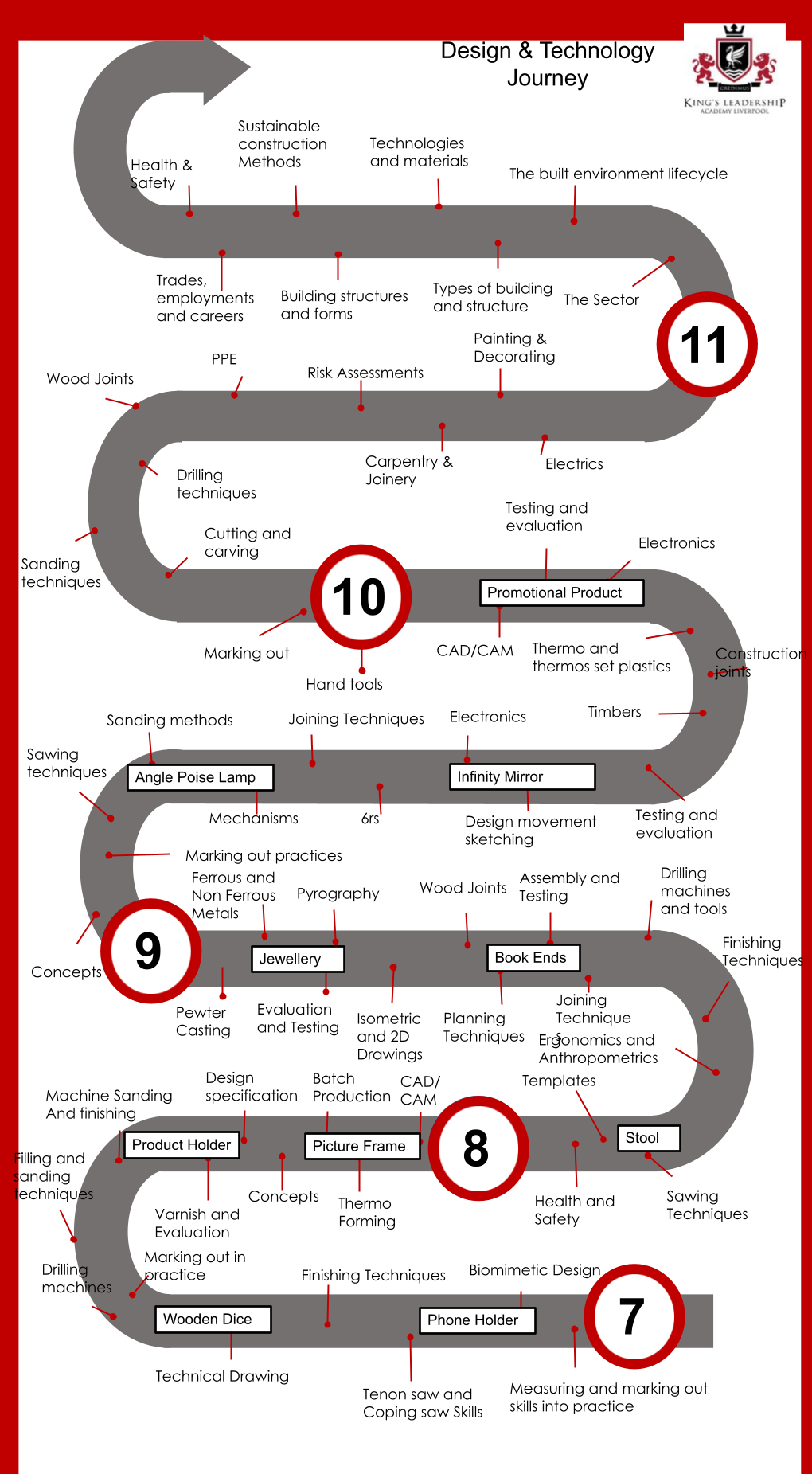
Year 7
Topics
- Biomimicry: Design inspired by nature (e.g., phone holder made from wood).
- Woodworking: Cutting, shaping, and joining wood to create products (e.g., phone holder, wooden dice).
- Technical Drawing: Creating accurate design plans and diagrams.
- Forming and shaping plastics: Moulding, shaping, and joining plastic materials for design projects.
- Product Design: Planning and making functional objects through iterative processes.
- Evaluation: Assessing and refining designs based on feedback and performance.
Skills
Biomimicry and Nature-Inspired Design
Pupils will observe natural forms and systems, learning to incorporate nature-inspired ideas into their designs. By creating items like a phone holder based on natural shapes, they’ll explore sustainable design and understand how nature can enhance functionality and aesthetics.
Woodworking Techniques
Pupils will practice cutting, shaping, and joining wood, learning essential woodworking skills and tool safety. Projects like making a wooden phone holder or dice will develop precision and craftsmanship as they work with a versatile, tactile material.
Technical Drawing and Design Visualization
Pupils will learn technical drawing basics, producing accurate design plans and diagrams. This skill enables them to communicate and visualize their ideas clearly, ensuring their designs are precise and achievable.
Plastics Shaping and Moulding
Working with plastics, pupils will practice shaping, moulding, and joining techniques. They’ll gain practical experience with synthetic materials, understanding how to manipulate them for specific design projects.
Product Design Process and Iterative Development
Pupils will follow a structured design process, from brainstorming to prototyping, refining products to meet user needs. This teaches creativity, project management, and adaptability through hands-on experience.
Evaluation and Refinement
Pupils will learn to assess and improve their designs based on feedback, enhancing both functionality and aesthetics. This process encourages critical thinking and a commitment to continuous improvement.
Year 8
Topics
- Building a wooden stool
- Designing & making decorative bookends
Skills
Creative Design
Developing original concepts for the stool and bookends, focusing on both functionality and aesthetics.
Technical Drawing
Creating detailed, accurate drawings that outline dimensions, shapes, and assembly methods for both projects.
Measurement and Marking Out
Accurately measuring and marking wood according to technical drawings to ensure precise cuts and assembly.
Woodworking Techniques
Learning how to use various tools for cutting, shaping, and finishing wood, including sanding and smoothing edges.
Joinery Skills
Mastering techniques such as finger joints for the bookends and appropriate joinery for the stool, ensuring strong and stable connections.
Assembly
Putting together the components of both projects using correct methods and ensuring structural integrity.
Finishing Techniques
Applying finishes such as sanding, staining, or varnishing to enhance the appearance and durability of the wooden products.
Testing
Evaluating the functionality and stability of the stool and bookends, checking for comfort, usability, and structural integrity.
Human-Centered Design (Ergonomics and Anthropometrics)
Applying principles of ergonomics to ensure the stool is comfortable and fits the needs of users, utilizing anthropometric data to determine appropriate dimensions (e.g., seat height, width) for a broad range of users.
Evaluation and Reflection
Assessing the final products for functionality, stability, and design effectiveness, and reflecting on what could be improved in future projects.
Year 9
Topics
- Angle-poised lamp
- Infinity Mirror
Skills
Creative Design:
Developing original concepts for the lamp, focusing on both functionality and aesthetics while incorporating design principles from 20th-century design movements.
Technical Drawing:
Creating detailed, accurate drawings that outline dimensions, shapes, and assembly methods for the lamp, guiding the construction process.
Measurement and Marking Out:
Accurately measuring and marking wood and other materials according to technical drawings to ensure precise cuts and assembly.
Woodworking Techniques:
Gaining hands-on experience in cutting, shaping, sanding, and finishing wood components to create a polished final product.
Joinery Skills:
Learning different methods for joining wood, such as doweling and using screws or adhesives, to ensure the lamp's structure is strong and stable.
Upcycling Techniques:
Understanding how to repurpose materials creatively, applying the principles of the 6Rs (Reduce, Reuse, Recycle, Repair, Refuse, and Redesign) to promote sustainability in design.
Electronics Proficiency:
Gaining knowledge of basic wiring and circuitry necessary for integrating electrical components, including sockets, switches, and bulbs, while adhering to safety standards.
Understanding Mechanisms and Motion:
Studying the principles behind the mechanisms that allow the lamp to adjust and maintain its position, including pivot points and levers, to enhance functionality.
Testing and Evaluation:
Assessing the lamp's functionality, stability, and design effectiveness through testing, followed by reflecting on successes and areas for improvement in the design process.
Assessment
Verbal feedback throughout the year
Self assessment of practical
End of unit test and assessment of overall final product to provide combined outcome.
The test includes multiple-choice, short-answer, and long-answer questions, covering theoretical knowledge from the course as well as materials and manufacturing methods studied.Practical work is assessed based on the quality of the final outcome, accuracy of cutting and joining, finishing techniques, creativity, and how well the product functions when tested.
GCSE (Years 10-11)
In the Eduqas Level 1/2 Construction course, students are introduced to a variety of topics that equip them with the knowledge and skills necessary for understanding and engaging in construction-related activities. Here are the key topics typically covered in the curriculum:
Topics
- Construction Materials
- Tools and Equipment
- Construction Techniques
- Building Regulations and Health & Safety
- Planning and Design
- Environmental Impact
- Project Management
- Structural Principles
- Finishing Techniques
- Evaluation and Reflection
Skills
-
Technical Drawing Skills:
Students learn to create and interpret technical drawings and blueprints. This includes understanding scale, dimensions, and symbols used in architectural plans, which is essential for successful construction projects. -
Measurement and Calculation:
Accurate measurement and calculation are crucial in construction. Students develop skills in measuring lengths, areas, and volumes, as well as calculating quantities of materials needed for projects. -
Hand and Power Tool Proficiency:
Students gain hands-on experience using a variety of hand tools (e.g., saws, chisels) and power tools (e.g., drills, routers). They learn proper techniques, maintenance, and safety practices for each tool. -
Joinery and Assembly Techniques:
This involves learning various methods for joining materials together, such as woodworking joints (e.g., dovetail, mortise and tenon) and assembling components to create stable structures. -
Problem-Solving and Critical Thinking:
Students enhance their ability to analyze situations, troubleshoot issues, and devise solutions during the construction process. This skill is crucial for adapting to challenges that arise on-site. -
Health and Safety Awareness:
Understanding and applying health and safety regulations is vital in construction. Students learn to conduct risk assessments, use personal protective equipment (PPE), and adhere to safe working practices. -
Project Planning and Management:
Students develop skills in planning construction projects, including scheduling tasks, budgeting, and managing resources. This includes learning to set realistic timelines and monitor progress. -
Environmental Awareness:
Students learn to consider the environmental impact of construction practices, including waste management, sustainable materials, and energy-efficient designs. This skill fosters a responsible approach to construction. -
Finishing Techniques:
Students practice various finishing techniques, such as painting, plastering, and tiling, to enhance the aesthetic and functional qualities of their constructed projects. -
Evaluation and Reflective Practice:
Students learn to assess the quality of their work and reflect on their construction processes. This includes identifying successes and areas for improvement, fostering a mindset of continuous learning.
These skills collectively prepare students for further studies in construction or entry-level positions in the industry, emphasizing both technical proficiency and a responsible, collaborative work ethic.
Assessment
The Eduqas Level 1/2 Construction qualification typically includes a combination of externally assessed exams and internally assessed controlled tasks. Here's an outline of the assessment structure:
1. Unit 1: Safety and Security in Construction
-
Type: Externally assessed written exam.
- Focus:
- Health and safety regulations.
- Risk assessments and safe working practices.
- Site security and protecting personnel and materials.
- Marks: Approximately 60 marks.
- Duration: Around 1 hour 30 minutes.
- Weighting: 25% of the overall qualification.
2. Unit 2: Developing Construction Projects
-
Type: Internally assessed controlled assessment.
- Focus:
- Practical skills in a chosen construction discipline (e.g., carpentry, bricklaying, painting and decorating).
- Planning, executing, and evaluating a construction project.
- Components:
- Producing a project plan.
- Using tools, materials, and techniques to create a construction task.
- Reflecting on quality and performance.
- Marks: Typically around 100 marks.
- Duration: Approximately 12 hours under supervised conditions.
- Weighting: 50% of the overall qualification.
3. Unit 3: Planning Construction Projects
-
Type: Externally assessed scenario-based task.
- Focus:
- Understanding project requirements, planning processes, and resource management.
- Producing risk assessments, schedules, and budgets.
- Application of knowledge to a given construction scenario.
- Marks: Approximately 60 marks.
- Duration: Around 2 hours.
- Weighting: 25% of the overall qualification.
Grading
The final grade is based on cumulative performance across all three components, typically awarded on a Level 1 Pass to Level 2 Distinction scale.
Clubs & Trips
Catch-up lessons are scheduled on Wednesdays during Term 3, Week 2, from 3:30 to 4:30 PM. These sessions provide pupils with dedicated time to focus on developing both their theoretical understanding and practical outcomes across Key Stages 3 and 4.
There are a variety of STEM competitions throughout the year. These competitions allow pupils to apply their knowledge and skills in real-world contexts, fostering creativity, teamwork, and problem-solving abilities. Participating in these events not only enhances their learning but also helps build confidence and enthusiasm for the subjects of science, technology, engineering, and mathematics.
Careers
- Product Designer
- Designing and developing innovative products for consumer or industrial use.
-
Architect
- Planning and designing buildings, considering functionality, aesthetics, and sustainability.
-
Civil Engineer
- Designing and overseeing infrastructure projects like bridges, roads, and buildings.
-
Graphic Designer
- Creating visual content for branding, advertising, and digital platforms.
-
Interior Designer
- Designing functional and visually appealing interior spaces.
-
Automotive Engineer
- Developing and improving vehicle design, systems, and safety features.
-
Construction Project Manager
- Overseeing construction projects from planning to completion, ensuring timelines and budgets are met.
-
Textile Designer
- Creating designs for fabrics used in fashion, upholstery, or industrial applications.
-
Industrial Engineer
- Optimising manufacturing processes and product design for efficiency and quality.
-
Jewellery Designer
- Crafting and producing custom jewellery using traditional and modern techniques.
Homework & Revision
Homework
Set day: Week 1 Tuesday
Due day: Week 2 Wednesday
Format/platform: Class charts and classroom
Revision
https://www.technologystudent.com/
https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/subjects/z23vkhv
Wider Reading
Cradle to Cradle
James Dyson Invention
The design of every day things
Great designs
Engineers making a difference
Learning Journeys